-
Courses

Courses
Choosing a course is one of the most important decisions you'll ever make! View our courses and see what our students and lecturers have to say about the courses you are interested in at the links below.
-
University Life

University Life
Each year more than 4,000 choose University of Galway as their University of choice. Find out what life at University of Galway is all about here.
-
About University of Galway

About University of Galway
Since 1845, University of Galway has been sharing the highest quality teaching and research with Ireland and the world. Find out what makes our University so special – from our distinguished history to the latest news and campus developments.
-
Colleges & Schools

Colleges & Schools
University of Galway has earned international recognition as a research-led university with a commitment to top quality teaching across a range of key areas of expertise.
-
Research & Innovation

Research & Innovation
University of Galway’s vibrant research community take on some of the most pressing challenges of our times.
-
Business & Industry

Guiding Breakthrough Research at University of Galway
We explore and facilitate commercial opportunities for the research community at University of Galway, as well as facilitating industry partnership.
-
Alumni & Friends

Alumni & Friends
There are 128,000 University of Galway alumni worldwide. Stay connected to your alumni community! Join our social networks and update your details online.
-
Community Engagement

Community Engagement
At University of Galway, we believe that the best learning takes place when you apply what you learn in a real world context. That's why many of our courses include work placements or community projects.
Living Laboratory
The Engineering building at NUI Galway, which was opened in July 2011, consolidates education and research activities in the various engineering disciplines into one building, which not only provides a learning environment, but itself acts as a teaching and learning tool. It is serving as a ‘living laboratory’ for engineering, where live data sets from numerous types of sensors are being used to illustrate structural engineering and building performance concepts in undergraduate teaching and in the development of full-scale research in structural engineering and energy. The building contains green-building initiatives, which will provide working models for students. Several of the building’s constructional elements have consciously been left exposed, as visual learning tools (RMJM, 2008).
Both energy and structural characteristics of the structure are to be monitored throughout the buildings entire life cycle. The vision is for a building whereby future students will be able to analyse and understand a building’s defining characteristics at first hand and on a personal level. Data measuring the strains, temperatures and movements due to loading of the building are being gathered along with energy demands and performance of the building. Embedded sensors within structural elements are fundamental to the development of the building as an interactive teaching tool, reporting on the evolving dialogue of the structure with its environment (Goggins et al, 2012).
- Several major structural elements were instrumented in order to provide the interactivity required of the 'living laboratory'. Four elements were selected for instrumentation: a 40-tonne pre-tensioned reinforced concrete box beam, a pre-tensioned double-tee reinforced concrete unit, a novel precast two-way flat slab reinforced concrete system and a structural steel ‘hanging’ system with steel roof truss.spects instrumented as teaching and learning tools include:
- Light sensors automatically measure LUX in a room and operate lighting accordingly
- Occupancy sensors adjust temperature and turns occupancy sensors adjust temperature and turn off lights when a room is not in use
- Room temperature sensors for minimal energy consumption to monitor air quality
- Passive ventilation will cool room and reduces the need for air-conditioning
- Meters on water
- Meter on electricity
 Instrumented 40-tonne prestressed concrete transfer beam |
 Instrumented prestressed tee beam unit during fabrication at Banagher Concrete |
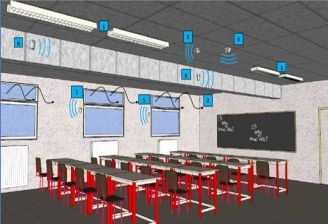 Schematic of various sensors in a teaching space in the new engineering building |
installedinthevoidformedflatslabsystemintheneb.jpg) Strain and temperature sensor (vibating wire guage) installed in the void formed flat slab system in the new engineering building |
The NEB uses an advanced CylonBMS to monitor and control the building. This displays real time measurements of building performance, as well as short and long-term trends.
- Electricity metering: total of 78 individual meters distributed by system and floor;
- Heat energy metering: total of 12 meters across both the hot and chilled water circuits;
- Internal environment parameters available in each zone: Temperature, Relative humidity (where relevant), CO2 concentration and window position (where relevant);
- Extensive sensor measurements of all HVAC systems;
- Internal slab temperature sensors: 5 per floor;
- Local weather monitoring station;
- Water monitoring;
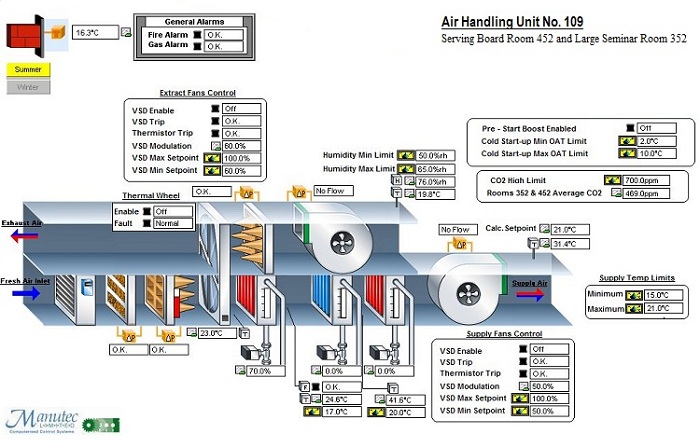
BMS DATABASE
An MySQL database stores long term BMS data from approximately 4,000 sensors and components installed throughout the building. This provides an invaluable asset for research (and education) related to building energy consumption, thermal comfort, and internal enviromental quality. If you are interested in gaining access to the NEB BMS database for research or education purposes, contact one of the following with your proposal.
Email: iruse@universityofgalway.ie















